Overview
Ignoring AI in Implementation is a big mistake
Whether or not you have a good plan, the result always depends on implementation

AI is set to redefine Education
Implementation Strategies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing education by enhancing the assessment process through advanced automated scoring and personalized feedback. However, there are many barriers to implementation including institutional support, faculty discomfort, and ethical considerations. Ever once these barriers are overcome though, implementation still requires careful consideration and forethought. Determining goals, collaboration with stakeholders, and pilot projects should be utilized to increase the likelihood that implementation will succeed.
Luckily, AI in education is a topic that provokes extensive research and implementation frameworks are starting to be developed. To effectively implement AI assessment tools, it is important to follow a structured framework and address both the benefits and challenges. This guide will help educators and institutions navigate the integration of AI in educational assessments, focusing on the evidence-centered design (ECD) framework presented by Ercikan et al., (2021).
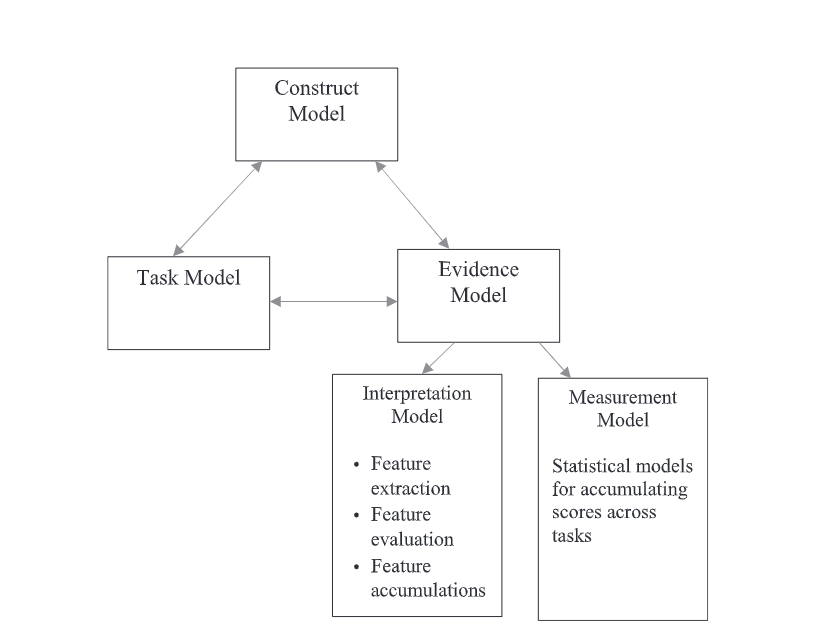
Evidence-Centered Design (ECD) Framework
The ECD framework is central to optimizing the implementation of AI-based automated scoring. This framework ensures that assessments are designed with AI capabilities in mind from the outset, aligning tasks with constructs and evidence models.
Key Facets of ECD
1. Pilot and Validate: Implement pilot tests to evaluate the effectiveness of the AI scoring system. Use these trials to refine algorithms, address any biases, and ensure the scoring process is fair and accurate (Ercikan et al., 2022).
2. Define Constructs and Competencies: Identify the skills and knowledge that the assessment aims to measure. Clearly defining these constructs is crucial for developing tasks that align with the desired outcomes.
3. Develop Task Models: Create assessment tasks that elicit evidence of the defined constructs. These tasks should be designed to capture the required performance data that AI can analyze.
4. Specify Evidence Models: Outline the types of evidence that will be used to make inferences about student performance. This includes identifying the data points that AI will evaluate to score responses accurately.
5. Design the Scoring Model: Develop algorithms and rubrics for AI to use in scoring assessments. Ensure that these models are transparent and can be validated to maintain the validity and reliability of scores.
By following the ECD framework,
educators can create AI assessment tools that provide consistent, objective scoring,
reduce administrative burden, and support valid inferences from assessment
data.

References
Ercikan, K., Simon, M., & Oliveri, M. E. (2022). Optimizing implementation of artificial‐intelligence‐based automated scoring. Journal of Educational Measurement, 59(1), 7-25. https://doi.org/10.1111/jedm.12290
Kulasegaram, K., & Rangachari, P. K. (2019). Challenges of implementation of artificial intelligence in medical education. Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development, 6, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1177/2382120519889340
Slimi, Z. (2021). The impact of AI implementation in higher education on educational process future: A systematic review. University of Deusto. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1081043/v1
Addressing Challenges and Ensuring Success
Implementing AI in assessments also comes with challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful integration:
- Data Privacy and Security: Safeguarding student data is paramount. Institutions must implement security measures to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Technical and Operational Challenges: Developing and maintaining AI systems requires technical expertise. Collaborating with AI developers and investing in training for educators can help overcome these challenges.
- Transparency and Explainability: Ensuring that AI decision-making processes are transparent and explainable is critical. Educators should be able to understand and trust the AI systems used in assessments.
- Validation and Continuous Improvement: Regularly validate AI-based assessment tools through rigorous studies comparing them with traditional methods. Continuous improvement based on feedback and performance data will enhance the effectiveness of AI tools over time (Kulasegaram and Rangachari, 2019).
By embracing these guidelines and leveraging the ECD framework, educational institutions can harness the power of AI to transform the assessment process, providing students with personalized, equitable, and effective evaluations.

